In the US, Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) inflation data, which is critical for the Fed's monetary policy, came in above expectations. The significant slowdown in growth during the same period triggered a complex pricing process in the markets. According to the December data, core PCE inflation increased by 0.4% on a monthly basis. Market expectations were at 0.3%. The previous month's monthly increase was recorded at 0.2%. Annual core PCE rose to 3.0%, compared to an expected 2.9%. The previous data was 2.8%. A similar picture emerged in headline PCE. Annual PCE came in slightly above expectations at 2.9%, while the monthly increase was 0.4%. Thus, the gradual slowdown trend observed in recent months was interrupted. The continued price pressure, especially in services, indicates that inflation has not yet settled on a path consistent with the Fed's 2% target. According to the Kobeissi Letter, core PCE inflation has reached its highest level since November 2023. This development reveals that the disinflation process is not linear and that price pressures can occasionally regain strength.
The growth data released on the same day as the upward surprise in inflation indicated a loss of momentum in the economy. The US economy grew by only 1.4% in the fourth quarter, compared to an expected growth of 2.8%. This sharp slowdown, following the strong 4.4% performance recorded in the previous quarter, reflects the impact of weakening domestic demand and government spending.
While the resulting picture does not present a classic stagflation scenario, it points to a difficult balance for policymakers. Growth is slowing, but inflation is accelerating again. This situation represents a combination that could weaken the Fed's hand regarding interest rate cuts.
The market has recently been pricing in expectations of two interest rate cuts within 2026. The expectation of a June easing was particularly prominent. However, the monthly PCE increase of 0.4% and the annual level of 3.0% indicate that the "wait-and-see" period may be extended. An early interest rate cut may become more difficult without a sustained and strong decline in inflation.
Geopolitical risks are also affecting pricing in global markets. The escalation of tensions between the US and Iran is suppressing risk appetite, while US President Donald Trump stated that the process could be clarified within 10 days. These statements have made the already fragile market psychology even more sensitive.
How was the Bitcoin price affected?
The cryptocurrency market is also exhibiting a volatile appearance due to the influence of both macroeconomic data and geopolitical developments. Following the release of the PCE data, Bitcoin saw sharp movements and a search for direction.
In the initial price movements after the data, Bitcoin retreated from above the $68,000 level. As of the time of the news, the BTC price is trading at $66,554. During the day, the lowest level tested was $65,734 and the highest was $68,226. There has been a decline of approximately 0.67% in value over the last 24 hours.
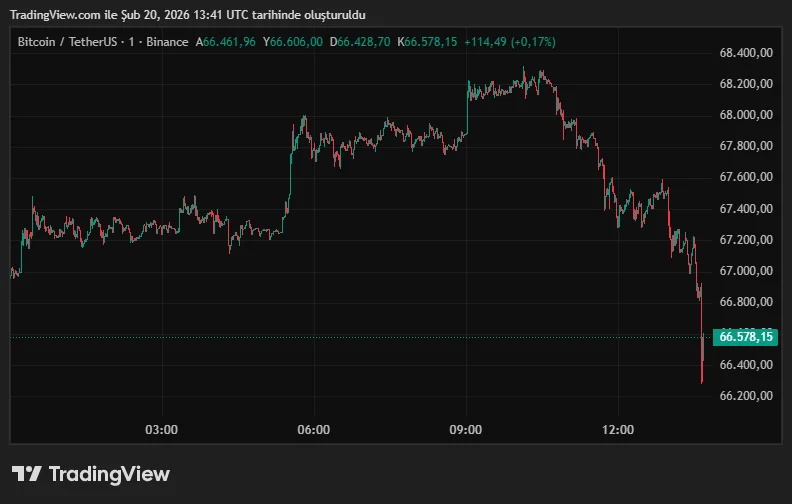
The higher-than-expected inflation data paved the way for a short-term strengthening of the dollar while putting pressure on risky assets. The pullback in Bitcoin reflected this macroeconomic pressure. On the other hand, the sharp slowdown in growth has not completely eliminated the pressure on the Fed to ease monetary policy in the medium term.



