Google's recently implemented Play Store policy change sparked widespread backlash among cryptocurrency developers and privacy advocates. By requiring licenses for wallet apps, the company failed to distinguish between custodial and non-custodial models. This risked effectively banning many non-custodial wallets in the US and EU, despite not being legally required to do so. Following the outcry, Google clarified that non-custodial wallets were excluded and promised to amend the policy.
Requirements Exceed US Legal Framework
According to the initial policy, all wallet developers in the US were required to obtain FinCEN's Money Service Business (MSB) registration and a state-by-state "money transmitter license." This effectively extended the anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements imposed on banks to all wallet apps. However, FinCEN's 2019 guidance clearly stated that non-custodial wallets, which do not hold or transfer user funds, are exempt from this classification. Although not legally required, the policy would force small developers to leave the Play Store and restrict users' access to privacy-focused tools.
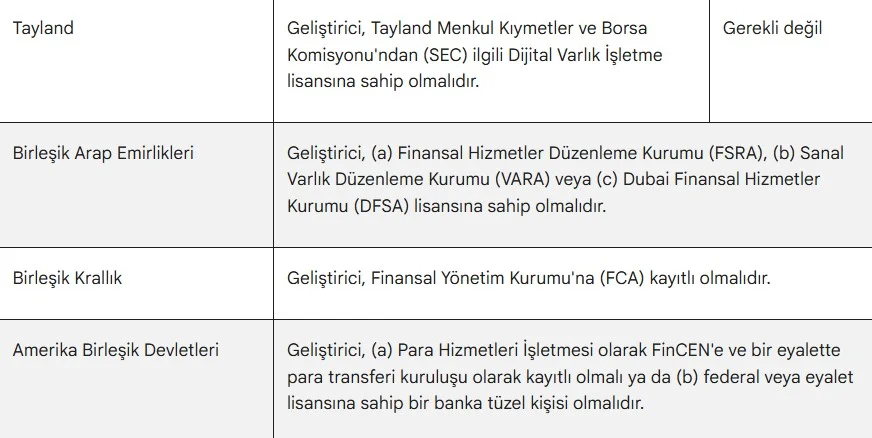
Risk of a de facto ban in the EU conflicting with MiCA
On the European Union side, Google's policy appeared to align with the "Crypto Asset Service Providers" (CASP) licensing system defined under MiCA. However, the CASP definition covers organizations that issue, exchange, or store digital assets. Because non-custodial wallets did not meet these criteria, obtaining a license was practically impossible. This meant they were removed from the EU Play Store. The only exception was if such wallets were distributed through a licensed CASP, which would have concentrated the market in the hands of large, regulated players.
FATF Impact and “Commercial Regulation”
The policy approach was very similar to the broader comments in the FATF’s 2021 guidance. The FATF had proposed that some non-custodial software developers involved in processes such as user interfaces, even if they don’t technically provide storage, be considered “Virtual Asset Service Providers.” While the FATF guidelines are not legally binding, member states can face sanctions if they fail to comply. Google’s inclusion of these standards in its app store rules has been characterized by critics as “commercial regulation.”
Why are they important for decentralization and privacy?
Non-custodial wallets are a cornerstone of the crypto ecosystem’s principle of “financial sovereignty.” These tools allow users to control their own keys and conduct transactions without relying on third parties. Applying bank-specific licensing regimes to these software could eliminate small projects and limit consumer options to strictly regulated applications with KYC requirements. This would be a major setback for innovation and privacy. Google's decision to backtrack and exempt non-custodial wallets from licensing is a positive development. However, this incident demonstrates that not only governments but also large tech companies can influence freedom of access and use in the crypto space. The infiltration of FATF-like frameworks into private sector policies could be seen as a sign that developers and users may be forced to fight the same struggle for privacy and autonomy, but on different fronts.




