Global trade is accelerating daily, but financial systems still operate with the cumbersome legacy of the old order. Payments take days, documents are lost in paperwork, and costs are rising. This is where the XDC Network comes into play. Responding to institutions' quest for speed, trust, and efficiency, this hybrid Layer-1 blockchain network combines the best aspects of public and private chains under one roof. It reduces cross-border payments to seconds, digitizes trade finance, and reduces transaction costs to nearly zero. Thanks to its Ethereum-compatible infrastructure, smart contracts run seamlessly on XDC, and its native token, XDC, is at the heart of this new digital financial system.
XDC Network Definition and Origins
Founded in 2017 by Atul Khekade and Ritesh Kakkad, XDC Network began its journey with the goal of transforming the slow, expensive, and complex financial systems of global trade. Khekade was an experienced entrepreneur in finance and technology, while Kakkad was an expert in cloud infrastructure and web technologies. The duo aimed to establish an ecosystem that would bring together governments, financial institutions, suppliers, and regulators on the same digital network. Developed with this vision, the XDC Network aims to bring speed and transparency to the global economy by providing a more efficient financial infrastructure.
Traditional trade finance still operates through documents, letters of credit, and paperwork. Payments take days, fees increase, and processes are prone to errors. The XDC Network breaks this chain. The network transforms commercial documents and financial instruments into digital tokens and brings them to the blockchain. This allows transactions to occur in seconds, reduces costs, and makes the entire process more transparent and traceable.
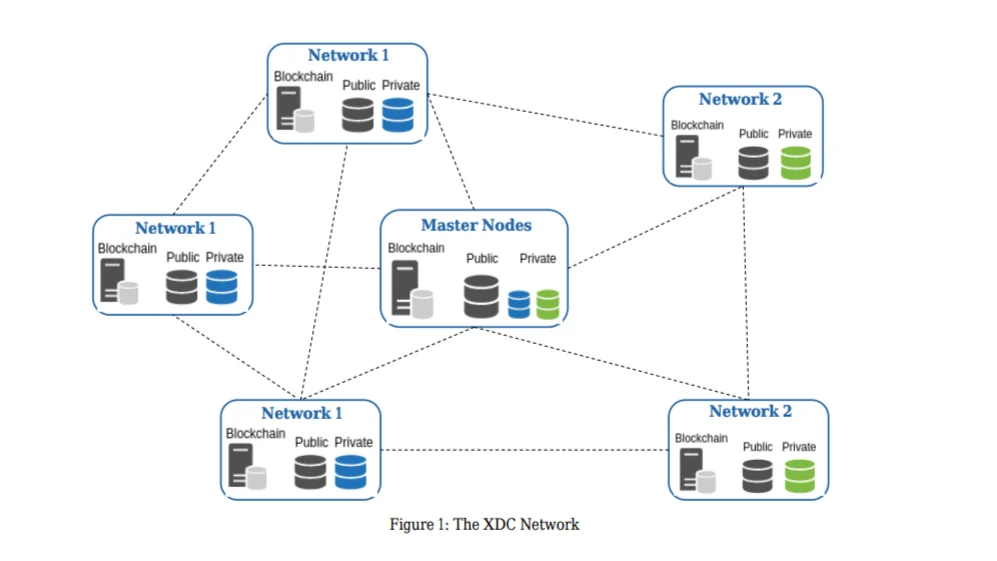
Thanks to its hybrid blockchain architecture, XDC provides full visibility into public transactions while also providing privacy to enterprises through dedicated subnets. This structure enables companies to comply with regulatory requirements without compromising data privacy. In short, the XDC Network stands as a blockchain infrastructure that redefines the balance of speed, security, and cost at an enterprise scale.
XDC Network History: Major Milestones
Since its launch in 2017, the XDC Network has grown steadily, becoming a major player in the global trade infrastructure. Here are the major milestones in the network's journey:
- 2017: The XinFin (eXchange inFinite) project was announced, and the foundations of the XDC Network were laid by Atul Khekade and Ritesh Kakkad. Initially, the Ethereum-based XDCE token was issued, with plans to later convert these tokens into XDC mainnet tokens on a 1:1 basis.
- June 1, 2019: The XDC mainnet officially launched. This was the first concrete milestone in the project's goal of "bringing global trade to the blockchain." With the launch of the mainnet, XDC became an independent entity operating on its own chain.
- 2020: The XDC Network was cited as a case study in a report prepared by the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). The TradeFinex platform was featured in the WTO's book "Blockchain & DLT in Trade" as an example of blockchain applications in trade finance. This earned XDC recognition in the global trade community.
- 2021: The XDC Foundation was established to support the growth of the ecosystem. Established with grant support from XinFin, this foundation undertook community-driven development and ecosystem funding. That same year, XDC became the first blockchain project to join the Trade Finance Distribution Initiative (TFD Initiative) institutional trade finance consortium. In September, a bridge was created between R3's enterprise network, Corda, and XDC. This bridge made the XDC token available as a native payment instrument in the Corda ecosystem, establishing a direct connection between private enterprise networks and the public blockchain.
- 2022: The first security-backed tokens were launched on XDC. Tradeteq issued TRADA tokens, backed by traditional financial assets, on the XDC network. These regulatory-approved tokens securitized trade finance assets and opened them to investors. That same year, STASIS EURS, Europe's largest euro-backed stablecoin, began trading on XDC. This step demonstrated that XDC could be used for fiat-backed digital money transfers across multiple chains.
- 2023: The XDC ecosystem gained wider adoption in the enterprise space. In December, a digital trade transaction secured by an electronic bill of lading (e-BL) was executed on the XDC Trade Network in collaboration with Tradeteq and TradeFlow Capital. This transaction, which provided liquidity for a seven-day shipment period, demonstrated the practical benefits of XDC in trade finance. That same year, a partnership with Japan-based SBI Holdings launched SBI XDC Asia Pacific. This initiative accelerated enterprise integration in the Asian market.
- 2024: The XDC developer community announced the XDC 2.0 update, designed to improve the network's security and performance. Whitepapers published in December 2024 introduced a Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT)-based mechanism, advanced forensic monitoring, "guard nodes," and an automatic token burn system, in addition to the Delegated Proof of Stake system. These innovations increased the network's transaction finality and reduced block times to an average of 6 seconds. That same year, the Real World Assets (RWA) Accelerator Program was launched. XDC began providing funding and mentorship support to RWA startups by partnering with global accelerators like Plug and Play.
- 2025: The XDC Network celebrated its sixth anniversary as a mainnet. The total number of transactions exceeded 800 million, and RWA applications on the network grew globally. Brazil-based VERT Capital launched the first large-scale RWA application in Latin America by tokenizing approximately $1 billion in receivables and payables on XDC. During the same period, the UK-based Archax exchange tokenized money market products of major funds such as BlackRock, Fidelity, and State Street on the XDC network. This development signaled that global financial giants were actively using XDC. In July 2025, Binance.US listed the XDC token and launched XDC/USDT trading in the US market. This listing significantly increased XDC's liquidity and visibility.
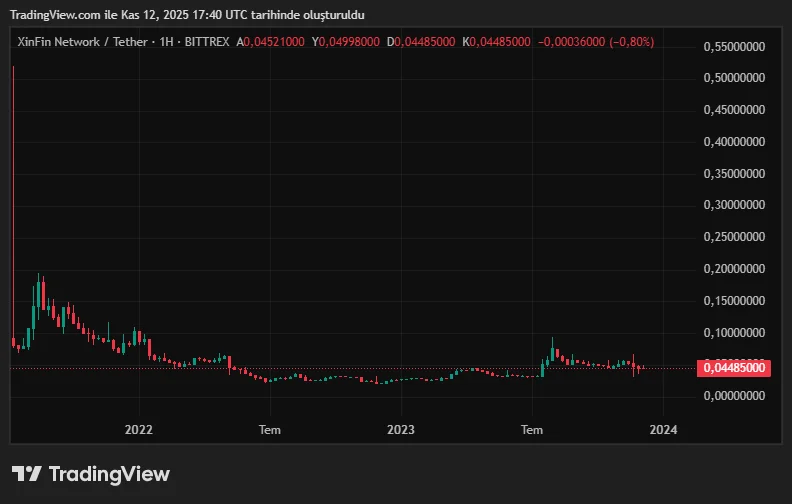
- As of November 2025, the XDC coin price is trading around $0.05. The coin has had a price chart like the one below since its launch.
Why is the XDC Network Important?
The XDC Network's value comes not only from its technical features but also from the real-world solutions it offers. The network has a wide range of uses, both for businesses and individuals. This transforms it from a simple Layer-1 platform into a part of the global financial infrastructure.
Cross-border Payments
Cross-border payments are one of the most time-consuming areas in global trade. In traditional systems, a transfer can take days to complete, and intermediaries like SWIFT charge high fees. The XDC Network changes this. Thanks to its ISO 20022 messaging standard-compliant architecture, banks can process transfers over the XDC network in seconds. For example, the network's Impel platform allows institutions to make payments with both USD-backed stablecoins and the XDC token, making transactions fast, transparent, and cost-effective. XDC's value in this area stems from its direct response to the "efficiency and speed" challenge that has plagued the financial world for years.
Smart Contracts
Because the XDC Network is compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), developers can easily port their dApps to the network. Smart contracts written in Solidity run on XDC, with near-zero transaction costs. This creates an attractive platform for DeFi protocols, NFT marketplaces, gaming projects, and enterprise applications. In other words, XDC isn't just a network focused on corporate finance; it also offers a scalable, fast, and affordable ecosystem for developers.
Trade finance
XDC Network's strongest area is the financing of global trade. Today, many export and import transactions are still conducted with paper documents, and letters of credit processes take weeks. XDC replaces this legacy system with a digital, blockchain-based model. Invoices, checks, and promissory notes can be tokenized and offered to global investors through platforms like TradeFinex. This allows an exporter to convert their receivables into digital assets with just a few clicks, providing instant liquidity. XDC's participation in international consortia like the TFD Initiative further strengthens its role as a standard-setter in trade finance. This field is measured in trillions of dollars, so XDC's position in this field directly increases the economic value of the network.
Tokenization
The future of traditional finance is being shaped by the concept of "tokenization," and XDC is at the center of this transformation. Creating digital representations of physical or financial assets on the blockchain offers significant advantages to both investors and issuers. Comtech Gold, operating on XDC, has launched CGO tokens, each backed by 1 gram of 24-karat gold. Similarly, the UK-based Archax exchange tokenized the money market funds of giants like BlackRock and Fidelity on the XDC network. Assets such as real estate, bonds, commodities, and even carbon credits can be represented this way. Thanks to tokenization, these assets become tradable 24/7, increasing transparency and making the financial world more liquid.
The Role of the XDC Token
XDC is used to pay transaction fees on the network, run smart contracts, and transfer value. Here, XDC takes on the same function as ETH on Ethereum. Token holders participate in the network's consensus process by staking their XDC, contributing to network security and earning rewards in return. XDC is also used as a governance tool for community votes and network protocol updates. This means users don't just hold tokens; they can directly shape the future of the network.
Supply Model and Burning Mechanism
XDC's total supply is estimated at approximately 37–38 billion units. As of 2025, approximately 17.7 billion of this amount are in circulation. The remainder is gradually incorporated into the system through rewards and incentive programs. The model is built on a balanced inflation and deflation structure. Validating nodes earn XDC as rewards for producing new blocks, while a portion of transaction fees are burned (permanently removed from the system) to keep the supply under control.
With the XDC 2.0 update, announced in 2024, this burning mechanism will be automated. A certain percentage of the fees collected in each block will be burned at a rate determined by the community. This way, as network usage increases, XDC will become deflationary. Combined with low transaction fees, this model offers a predictable and sustainable economic structure for institutional users.
Staking and Network Security
The XDC Network uses a consensus mechanism called XinFin Delegated Proof of Stake (XDPoS). In this system, validators (masternodes) who protect the network verify transactions by staking a minimum of 10 million XDC. The high staking requirement increases the cost of malicious behavior, making the network resilient to attacks.
Currently, there are over 100 active validators on the network. In addition, backup structures called "guard nodes" are in place, ensuring the uninterrupted operation of the network. Honest validators earn rewards for each block, while nodes that make erroneous transactions or attempt to manipulate the system face slashing (penalties). This system both strengthens security and incentivizes participants to act honestly.
In terms of energy efficiency, XDC is far ahead of traditional blockchains. It consumes a million times less energy than Proof of Work systems. This environmentally friendly structure aligns with sustainability standards, which are particularly important for institutional investors.
Ecosystem Incentives
The XDC Network has established a vibrant ecosystem not only technically but also in terms of community and innovation. The XDC Foundation, established in 2021, accelerates the network's growth by providing grants to developers and projects. Teams working in the DeFi, NFT, and RWA (real-world assets) space utilize these funds to build their products on XDC.
Bug bounty programs, hackathons, and accelerator collaborations are organized to keep the community active. Developers are rewarded with XDC for discovering vulnerabilities or developing new solutions. In 2024, the hybrid oracle project Plugin and the NFT/DeFi initiative Prime Numbers benefited from these incentives and grew.
To expand the ecosystem globally, XDC partnered with accelerators like Plug and Play, providing investment, mentorship, and technical support to new ventures. These incentives create a continuous cycle of innovation within the ecosystem. Each new project increases the network's usage and, consequently, the demand for XDC.
XDC Network Developers and Leadership
XDC Network founders Atul Khekade and Ritesh Kakkad launched the project in 2017 with the vision of bringing finance and technology together. Khekade is an entrepreneur developing permissioned blockchain systems for banks in Asia, while Kakkad is a veteran of cloud technologies and network security. The project initially began at Singapore-based XinFin Fintech Pte. Ltd., then transitioned to a more transparent structure in 2021, establishing the XDC Foundation. The Foundation oversees developer relations, corporate collaborations, and global outreach activities.
Professor Pramod Viswanath from Princeton University led the technical development of XDC 2.0's BFT-based consensus protocol. André Casterman, with 20 years of SWIFT experience, serves as an advisor. In 2022, Japanese financial giant SBI Holdings became a strategic partner to support XDC's Asia-Pacific expansion, and in the Middle East, gold tokenization projects were developed with Comtech Gold. Thanks to the open source community and the XDC Improvement Proposal (XIP) system, the network's development is now shaped by global developers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Below are some frequently asked questions and answers about the XDC Network:
- What is the difference between XDC and Ethereum?: While Ethereum is a general-purpose network, the XDC Network focuses on trade finance and corporate payments. Ethereum has a transaction capacity of around 15–30 TPS and high fees, while XDC, with its Delegated Proof of Stake + BFT architecture, can process approximately 2000 transactions per second and costs under $0.0001. XDC's hybrid architecture supports private subnets, and thanks to its ISO 20022 compliance and R3 Corda integration, it can integrate directly with financial institutions.
- Where can I buy XDC tokens?: XDC is traded on global exchanges such as KuCoin, Bybit, Gate.io, and MEXC. It will also be listed on Binance.US by 2025. It may be available on some platforms in Turkey. Because XDC is compatible with Ethereum, it can also be purchased on DEXs with the wXDC version. However, the safest way to trade is through centralized exchanges.
- How many TPS does the XDC network have?: The network has a capacity of over 2000 transactions per second (TPS). Compared to Bitcoin's 7 TPS and Ethereum's 30 TPS, XDC is considerably faster. Its average block time is around 2 seconds. The upcoming XDC 2.0 update will provide instant transaction finality and further increase network capacity.
- Why do corporates use XDC?: XDC offers low cost, high speed, and privacy for corporate transactions. Thanks to its ISO 20022-compliant structure, it integrates with banking systems. Solutions like Impel are developing alternative payment channels to SWIFT. Thanks to its hybrid architecture, companies can transact on both private and public networks. Furthermore, R3 Corda integration and TradeFinex partnerships enable large institutions to actively use XDC.
- Is it possible to issue tokens on the XDC network?: Yes. XDC offers easy token creation thanks to the Ethereum-compatible XRC20 standard. Developers can issue their own tokens with a simple smart contract. It also supports the XRC721 (NFT) and XRC1155 multi-token standards. Projects such as Plugin (PLI), StorX (SRX), and EURS currently use these standards.
You can find the latest content, user guides, and analyses about XDC and enterprise blockchain solutions in the JR Kripto Guide series.