Loopring (LRC) is a layer-2 (L2) protocol based on zkRollup that runs on the Ethereum blockchain. Its primary goal is to make decentralized exchange (DEX) transactions faster, cheaper, and more secure. Users can trade as they wish while keeping their assets in their own wallets, thus maintaining control and avoiding high gas fees. Loopring offers an innovative infrastructure that reduces Ethereum's slowness and cost while preserving its security. The protocol's native cryptocurrency is LRC and operates in accordance with the ERC-20 standard.
The Loopring protocol utilizes zkRollup technology, one of Ethereum's scaling approaches. This technology allows it to aggregate slow and costly transactions on the Ethereum network, acting like a "bulk transport" system, enabling high speed and low fees. Loopring stands out as the first zkRollup-based DEX protocol on Ethereum. Unlike traditional DEXs, most transactions are processed outside of Ethereum and written to the chain in hash form, allowing you to trade in seconds with Loopring, and gas fees per transaction are quite low. Let's continue with our guide to learn more about Loopring, how it works, and explore its use cases.
Loopring's Definition and Origin
The Loopring protocol was first announced by Daniel Wang in August 2017. Wang, a software engineer with a background in Google and JD.com, realized the inherent problems inherent in centralized exchanges after encountering difficulties with the centralized crypto exchange he operated, Coin Port, in 2014. This experience sparked the idea of developing an exchange infrastructure that would allow users to have full control over their assets. Consequently, Wang began working on developing the Loopring concept, a decentralized exchange protocol.
Loopring's emergence is closely tied to developments in the cryptocurrency market in 2017. The project held an initial coin offering (ICO) in August 2017, raising approximately 120,000 ETH (approximately $45 million). However, due to restrictions imposed by the Chinese government on ICOs shortly thereafter, Wang and his team decided to return 80% of the funds raised to investors. With the remaining budget, development of the Loopring protocol continued, and the team managed to maintain its project goals despite limited resources.
You might be wondering where the name Loopring comes from. The project's name comes from a unique "ring-matching" method. In the first version of Loopring, multiple buy and sell orders could be matched to form a circular ring, enabling more efficient, direct exchange between different cryptocurrencies. This innovative approach offered the potential for both better price formation and higher liquidity. Over time, Loopring refined its technology based on this original idea and evolved into a much more efficient protocol running on Ethereum with zkRollup.
Loopring's History: Key Milestones
Loopring's history is also quite noteworthy. Let's take a look at the cryptocurrency's history together:
- 2017: The foundations of the Loopring protocol were laid. Daniel Wang announced the project, and an ICO held in August 2017 raised 120,000 ETH (approximately $45 million). Following China's ICO ban, the majority of the funds raised (80%) were returned, but project development continued with the remaining resources.
- 2018: Work continued on the initial versions of the Loopring protocol and its underlying infrastructure. This year, the project aimed to design its protocol, which operates on a ring-peering model, to be open to implementation on different blockchain platforms.
- 2019: With Loopring version 2.0, the protocol's token economy was updated; transaction fees can now be paid with different tokens, and a certain percentage is regulated by burning LRC. In May 2019, the LRC token contract was upgraded to version 2.0, adding a burn feature to the smart contract, allowing the LRC supply to decrease as the protocol is used.
- 2019-2020: The Loopring protocol upgraded to version 3.0, integrating zkRollup technology. This dramatically increased the protocol's transaction throughput (from the previous ~2-3 TPS to over ~2,000 transactions per second with zkRollup). This step, which achieved scalability while maintaining security, made Loopring a leader in the layer-2 DEX space.
- 2020: The Loopring ecosystem made significant strides. In June 2020, a feature called Loopring Pay was announced, enabling nearly free and instant Ethereum transfers on zkRollup (a single transaction fee of approximately $0.0001). In September 2020, Loopring became the first DEX protocol to integrate with Band Protocol and utilize cross-chain oracle price feeds. In November 2020, the beta version of the smart mobile wallet, Loopring Wallet, was released; this was the first smart wallet on Ethereum to include zkRollup scaling.
- 2021: The automatic market maker (AMM) feature was launched on the Loopring protocol. With the release of Loopring 3.6 in December 2020, both the order book model and AMM-based transactions were supported. This allowed users to execute transactions on Loopring L2 through liquidity pools similar to Uniswap.
- 2022: A development brought the name Loopring to the masses: Game retailer GameStop announced that it had built its NFT marketplace on Loopring. Launched in beta in March 2022, the GameStop NFT Marketplace ran on Loopring L2, offering users fast and low-cost NFT trading. That same year, Loopring founder Daniel Wang stepped down as CEO and moved into an advisory role, focusing on new projects (e.g., Taiko) on Ethereum Layer-2 technologies.
- 2023: The Loopring protocol continued to increase its transaction volume as one of the most efficient Layer-2 solutions on Ethereum. After exceeding 1 million NFTs minted on Loopring L2 in 2022, millions of transactions were processed on the DEX platform with low fees throughout 2023. Despite increasing competition, Loopring continued to offer its users a reliable L2 experience.
- 2024: In June 2024, a security breach occurred in Loopring's smart wallet application. An attacker targeted several wallets by exploiting a vulnerability in the two-factor authentication mechanism of Loopring Smart Wallet users. Following this incident, the team temporarily stopped the wallet's Guardian and 2FA-related operations and took steps to address the issue. The core protocol was not affected.
- 2025: In May 2025, the Loopring team announced that the Loopring Wallet mobile app would cease operations on June 30, 2025. Users were advised to transfer their wallet assets to alternative wallets (such as MetaMask or Rainbow) until then. This shutdown only affected the mobile interface, while Loopring's layer-2 protocol continues to function. The LRC coin price is currently at $0.6 as of November.

Why is Loopring Important?
The Loopring protocol holds a significant position in the crypto ecosystem thanks to both its technological innovations and the practical benefits it provides for users. Below, let's examine Loopring's use cases and why it has attracted attention in the context of the token economy.
Use Cases
- Decentralized Exchange (DEX) Platforms: Loopring can be used on various platforms as a DEX protocol. Developers can build their own decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges using the Loopring protocol. Loopring offers a DEX infrastructure that operates with an order book model, allowing users to trade using their familiar exchange interface but keeping their funds in their own wallets. Loopring Exchange, the official application of the Loopring team, is the protocol's reference exchange and enables the unsupervised trading of tokens on the Ethereum network.
- Payments and Transfers: In addition to buying and selling transactions, Loopring can also be used for sending payments as an Ethereum L2 solution. Thanks to the Loopring Pay feature, introduced in 2020, users were able to instantly transfer their assets to each other on Ethereum with virtually zero gas fees. For example, it was possible to transfer Ether or ERC-20 tokens with Loopring Pay for a negligible fee of $0.0001. This feature effectively made Loopring a "layer-2 payment network" for Ethereum.
- NFT and digital collectibles platforms: Loopring's scalable structure can also be integrated into NFT trading applications. In particular, the NFT marketplace launched by GameStop in 2022, operating on Loopring L2, provided speed and cost advantages in NFT transactions. The fact that over one million NFTs have been minted on Loopring early on demonstrates its potential in the NFT ecosystem. Thanks to low fees, artists and collectors have been able to interact without the restrictions of the Ethereum mainnet.
- Liquidity Pools and DeFi Applications: While the Loopring protocol initially used an order book model, it also integrated AMM (Automated Market Maker) support with version 3.6. This made it possible to swap tokens on Loopring L2 via liquidity pools similar to Uniswap. Loopring's flexible infrastructure facilitates interaction with different DeFi protocols, paving the way for various applications in the decentralized finance space.
- Loopring Wallet (Smart Wallet): The Loopring team developed a smart wallet application to enhance the user experience. This mobile wallet, called Loopring Wallet, brought the advantages of Ethereum Layer-2 to everyday use. Users could quickly buy and sell via the DEX integrated with Loopring Wallet and make instant transfers to other wallets via Loopring Pay. The wallet aimed to expand the use of cryptocurrency by enhancing security with features such as social recovery. Although the Loopring Wallet implementation was discontinued in 2025, this wallet concept provided a good example of how the Loopring protocol could be implemented in a user-friendly manner.
Token Economics
LRC, Loopring's native cryptocurrency, is designed to ensure the protocol's economic stability and incentivize user participation. The economic model of the Loopring token (LRC) can be summarized as follows:
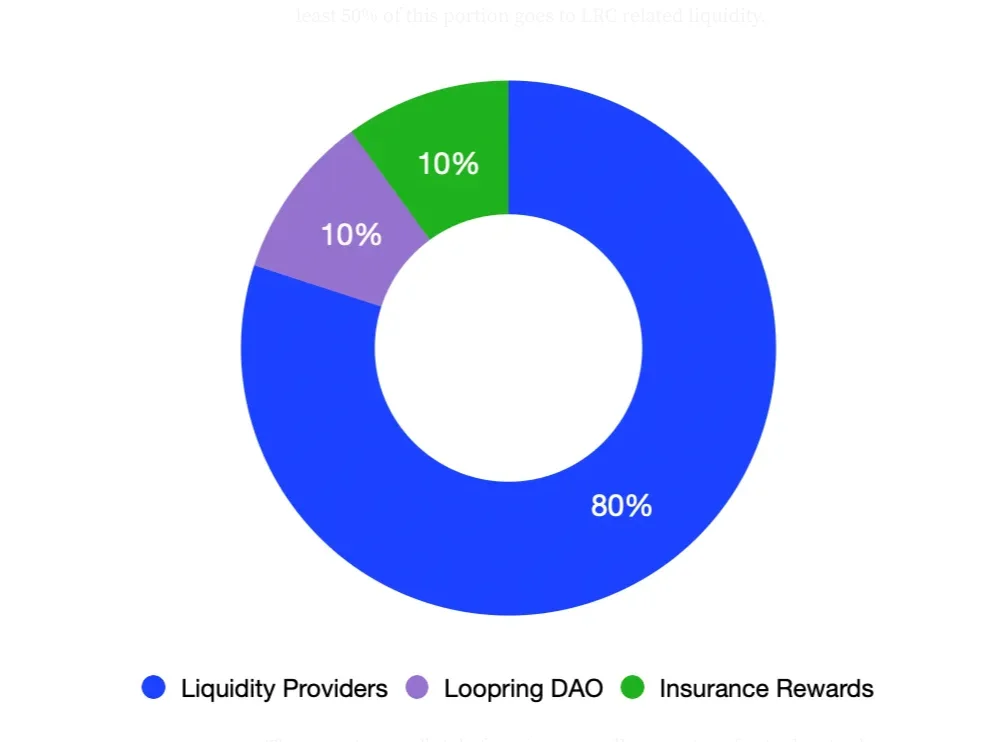
- Staking and reward distribution: LRC holders can earn a share of transaction fees on the Loopring platform by locking and staking their tokens in smart contracts on the protocol. According to the current model, 80% of the fees collected on the protocol are distributed as rewards to LRC liquidity providers, 10% is transferred to the community fund called the Loopring DAO, and the remaining 10% remains as insurance rewards. LRC staking transactions typically have a minimum lockup period of 90 days. This mechanism converts network usage into LRC demand, creating a deflationary effect for the token and rewarding long-term token holders.
- DEX operator collateral: Those wishing to operate a decentralized exchange built on the Loopring protocol must lock a certain amount of LRC as collateral. For example, to launch a DEX on Loopring, an exchange operator must lock at least 250,000 LRC in a smart contract. If the operator wishes to operate in a mode that keeps all transaction data off-chain (for greater efficiency), staking up to 1,000,000 LRC may be required. This collateral is intended to ensure the operator's reliability; if the operator engages in activity contrary to the interests of users or attempts to abuse the system, the protocol may forfeit a portion of the LRC deposited, which may be distributed to eligible users.
- Supply and deflation: The LRC token was initially issued via an ERC-20 smart contract on Ethereum and has a maximum supply of 1.375 billion. During the 2017 ICO, a significant portion of the tokens were distributed to investors, and although funds were refunded due to regulations in China, the LRC community has grown over time. Due to the 10% token burns that occur as the Loopring protocol is used, LRC's circulating supply tends to gradually decrease. This means it's an economic model designed to have a positive long-term impact on the token's value. LRC is listed on major cryptocurrency exchanges and can be stored and transferred in all Ethereum-compatible wallets.
Who are the Founders of Loopring?
The team behind the Loopring project is critical to its success and security. Founder Daniel Wang was the originator and longtime leader of Loopring. A software engineer of Chinese origin, Wang has worked at tech giants such as Google and JD.com and has experience operating a centralized exchange. Wang's observation that the problems encountered with centralized exchanges were inevitable led him to design Loopring. In 2022, Daniel Wang stepped down as CEO of Loopring, remaining on the project as an advisor, focusing on the Taiko project, a new zkRollup initiative on Ethereum.
The Loopring team includes prominent figures besides Wang. Jay Zhou, the project's chief marketing officer (CMO), previously worked in PayPal's risk management unit and gained experience at Ernst & Young. Johnston Chen, the chief operating officer (COO), has senior-level experience in the technology sector and served as director of information systems at 3NOD. The Loopring project is run by the non-profit Loopring Foundation. The foundation's structure focuses on the protocol's open-source development and adopts a community-driven approach.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Below are some frequently asked questions and answers about Loopring:
- How does Loopring work?: Instead of writing transactions directly to the Ethereum main chain, Loopring aggregates them off-chain and transfers them to the mainnet in bulk. Users first deposit their funds into Loopring's smart contract, and then their buy and sell orders are matched in Loopring's off-chain system. Hundreds of transactions are sent to Ethereum as a single packet, and thanks to zkRollup, the transactions within this packet are verified and recorded on the chain. This method ensures fast and cost-effective transactions while maintaining security with Ethereum's assurances.
- What is zkRollup?: zkRollup (zero-knowledge rollup) is a second-layer technology used to enable scaling in blockchains like Ethereum. In this method, multiple transactions are aggregated and transmitted to the mainnet as a single transaction, and "zero-knowledge proofs" are used to prove the validity of the transactions within the packet. The term "zero-knowledge" refers to a method of proving the authenticity of information without revealing its content. As a result, zkRollup significantly increases transaction throughput and efficiency without compromising the network's security. Loopring is one of the pioneering projects that has successfully implemented zkRollup technology.
- Is using Loopring safe?: Yes, using Loopring is considered safe. The Loopring protocol relies on the Ethereum mainnet for security; the final settlement of transactions is always written to the Ethereum chain with cryptographic proofs. This makes it as secure against external tampering as Ethereum. Furthermore, Loopring smart contracts have undergone independent audits and are open-source. Because users hold their assets in their own wallets, they are not exposed to the hacking or bankruptcy risks associated with centralized exchanges. Of course, it is always important for users to maintain their own account security (e.g., private key or seed phrase protection).
- What is the LRC token used for?: LRC is the primary token of the Loopring ecosystem and has multiple uses. First, users who stake LRC can earn a portion of the transaction fees generated by Loopring DEXs. For example, 70% of the fees collected from all DEXs on the Loopring protocol are regularly distributed to LRC stakers. Second, LRC is required as collateral for those wishing to operate an exchange/app on Loopring; operators who lock up a certain amount of LRC can join the network. This serves as an incentive for operators to act honestly. Finally, because LRC has a limited total supply and is burned as soon as it is used, it can be viewed as an asset with the potential to maintain its value over the long term. You can purchase your LRC token from major exchanges and store it in Ethereum-compatible wallets.
- What is Loopring Wallet?: Loopring Wallet is a smartphone wallet application developed by the Loopring team. This Loopring wallet aims to provide users with Layer-2 features on Ethereum with an easy-to-use interface. With Loopring Wallet, users could connect to the Loopring DEX directly from the mobile app, instantly buy and sell, and also transfer tokens to other L2 users for free. The wallet also included innovative security features like social recovery and was released in beta at the end of 2020. However, the Loopring team decided to discontinue its operation in 2025. However, users can still access Loopring L2 through popular wallets like MetaMask.