The question of what DAI is is one of the most frequently asked questions by users seeking stable and reliable alternatives in the cryptocurrency world. DAI coin is a decentralized stable cryptocurrency with a collateralized stablecoin model running on the Ethereum network. Designed to remain fixed at $1, DAI operates without any central authority.
It's also crucial to understand that DAI was developed by MakerDAO, the first DAO—or decentralized autonomous organization—in the cryptocurrency ecosystem. As you'll see, decentralized, user-based governance plays a critical role in DAI.
In this guide, we'll explore questions like "What is DAI coin?", "How does DAI work?", and "Why does DAI's price remain stable?" We'll also explore technical concepts such as the DAI coin collateral system, what is MakerDAO, and the RWA collateral model. Ready? Let's get started!
Definition and Origins of DAI
DAI was first created by MakerDAO in 2017. MakerDAO is a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) built on Ethereum and is the protocol behind DAI. So, if you're wondering what MakerDAO is, in short: MakerDAO is a system that allows users to generate DAI in exchange for collateral through smart contracts and manages DAI's stability. MakerDAO is a decentralized and autonomous protocol that uses collateralized debt positions (CDPs) to ensure the stability of the DAI stablecoin. Through its DAO structure, community members provide governance by voting on system parameters and protocol changes with MKR tokens.
Started by Danish entrepreneur Rune Christensen, this protocol eliminated traditional financial intermediaries, allowing users to self-create a stablecoin.
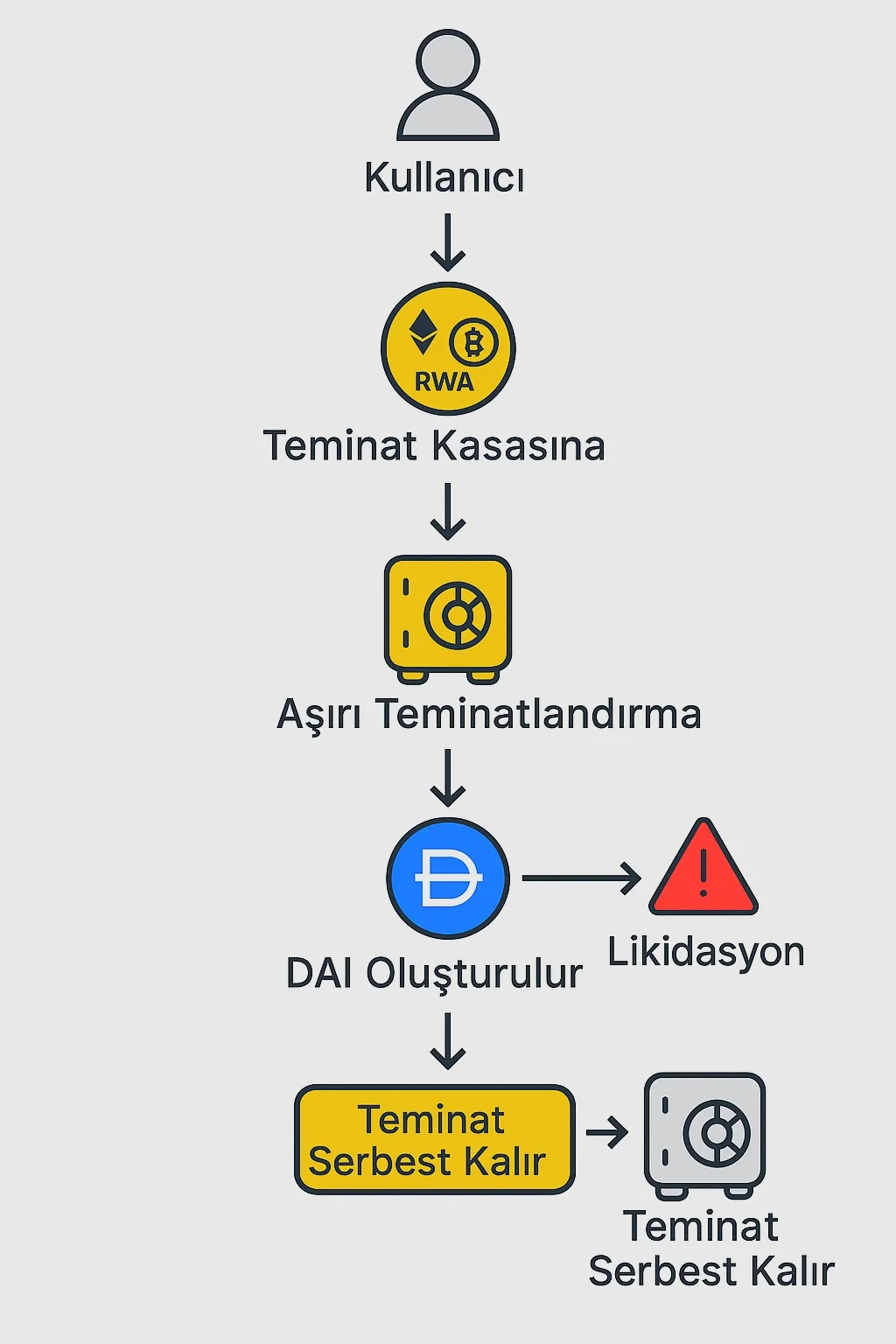
When we look at how DAI technically works, we encounter the collateralized stablecoin model. Essentially, the DAI collateral system is based on users locking their cryptocurrency assets into a smart contract and generating DAI in return. In other words, DAI is created by providing assets of another value as collateral. Users can borrow DAI in return by locking crypto assets (e.g., Ether or other tokens) accepted into MakerDAO's smart contracts on the Ethereum network.
This process can be roughly described as "minting DAI," but it's not a central authority that issues DAI, but rather the users themselves. So, if you're wondering who issues DAI, the answer is simple: There's no company or bank directly issuing DAI. Users create the coin through the protocol. For example, it's possible to generate stablecoins in exchange for ETH as collateral in the system: A user locks a certain amount of Ether in a vault and generates DAI corresponding to a certain percentage of it through the smart contract. The user can spend the DAI they obtain as they wish or use it in different DeFi protocols; when they want to reclaim their collateral, they can unfreeze the locked assets by paying back the DAI they generated (along with the interest accrued throughout the transaction).
DAI's collateral system is based on the principle of over-collateralization for security purposes. This means that collateral worth more than the amount of DAI produced is held in the system. For example, a user who wants to generate 100 DAI must generally lock up at least $150 worth of Ether as collateral. This ratio is called the collateralization ratio and is determined differently by MakerDAO governance for each collateral type (for example, the ratio can be 110% for some more stable assets, while it can be 150% or more for more volatile assets). Thanks to overcollateralization, even if the value of DAI declines, the collateral in the system remains sufficient to more than cover that value.
How does DAI work?
DAI maintains its $1 value through the automated operations of smart contracts and market dynamics. For example, if the market price of DAI falls below $1, users will buy cheap DAI to pay off their debts, reducing the amount of DAI in circulation and pushing the price back closer to $1. Conversely, if DAI rises above $1, arbitrageurs can profit by depositing collateral, producing 1 DAI at a cost of $1, and selling it on the market at a slightly higher price. This increases supply and lowers the price. Furthermore, MakerDAO influences DAI demand by adjusting fee rates (the so-called "stability fee," similar to the borrowing interest rate) and savings rate (DAI Savings Rate (DSR) to maintain DAI's stability. For example, if DAI demand is low, DSR is increased to provide interest incentives to DAI holders. If demand is high, borrowing fees are increased to slightly curb DAI production. These are all part of DAI's price stability mechanism.

DAI's History: Major Milestones
From humble beginnings in 2017, DAI quickly became the backbone of Ethereum-based financial applications. Each update, each newly integrated collateral type, and each governance decision enabled DAI to evolve into a technical ecosystem. Let's take a look at the key milestones of this impressive journey:
- 2017: The first version of DAI, Single Collateral DAI (SAI), was launched on the Ethereum mainnet. During this period, DAI was issued solely with Ether collateral. The Maker team, led by Rune Christensen, brought the concept of a decentralized stablecoin to life for the first time with this launch.
- 2019: The transition to Multi-Collateral DAI (MCD) was completed, and the system underwent a major update. With MCD, which went live in November 2019, various cryptocurrencies (such as BAT, USDC, and WBTC) began being accepted as collateral. This update also introduced the DAI Savings Rate (DSR), which allows DAI holders to earn interest. The old single-collateral DAI, called SAI, was discontinued, and all users transitioned to the new DAI system. The differences between DAI and SAI can be illustrated as follows:
Feature | SAI (Old DAI) | DAI (Current Multi-Collateral) |
Definition | Single-collateral legacy version of DAI | Decentralized stablecoin with multi-collateral backing |
Collateral Type | Only Ether (ETH) | ETH, wBTC, LINK, UNI, stETH, and other crypto assets |
Blockchain | Ethereum | Ethereum |
Governance | Initially launched by MakerDAO | Governed by the community via MKR token voting |
Status | Deprecated; exists for legacy users only | Actively used and developed |
Stability Mechanism | CDP (Collateralized Debt Position) | CDP + Risk parameters + on-chain governance |
- 2020: With the rise of DeFi (Decentralized Finance) applications, demand for DAI exploded. Many users began using DAI on lending/borrowing platforms, making it the preferred choice for liquidity pools. The supply of DAI increased rapidly, particularly during the summer of 2020, known as "DeFi Summer." During this period, incentive programs offered by platforms like Compound made it attractive for users to borrow and use DAI. Consequently, DAI has become a cornerstone of the DeFi ecosystem.
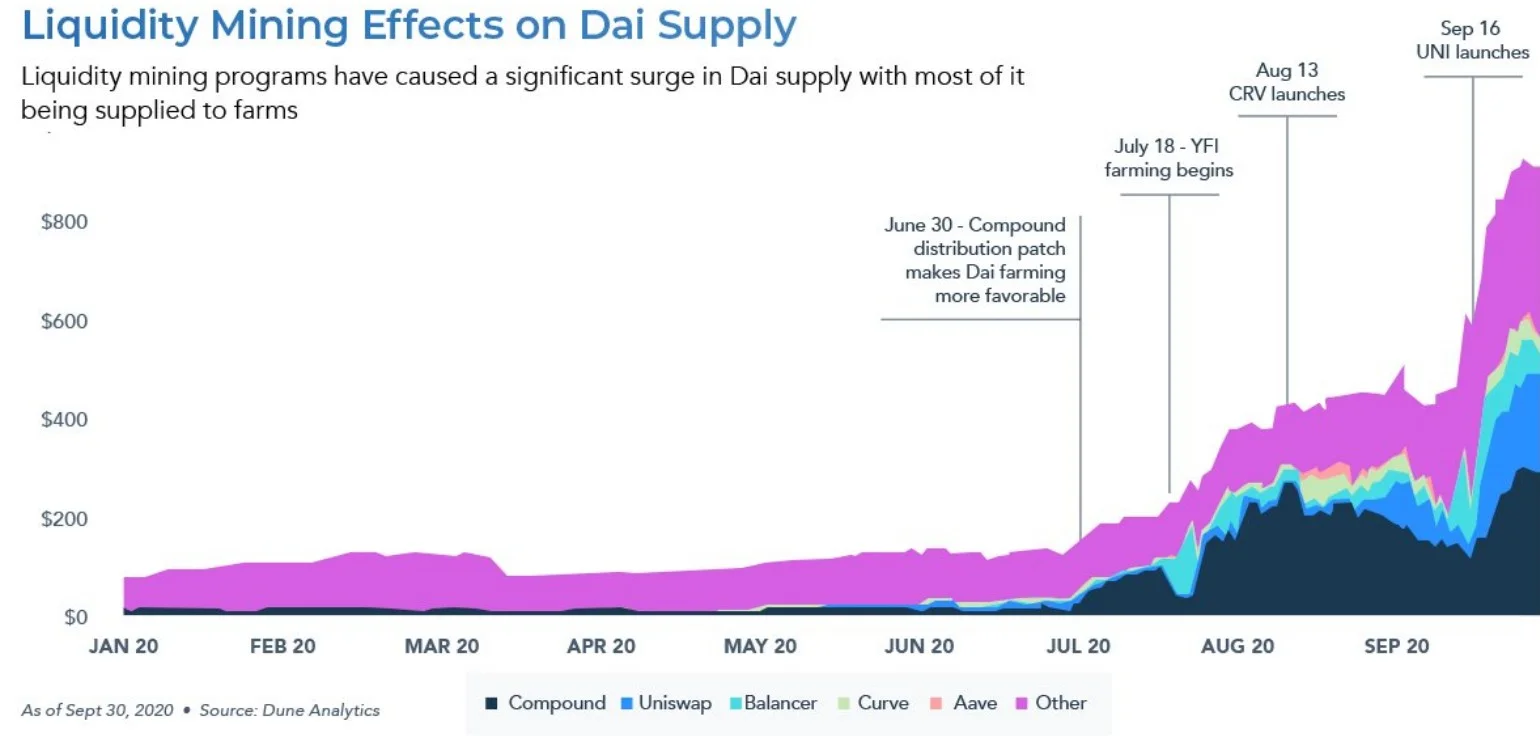
- 2021: DAI's market capitalization continued its steady growth, surpassing the $5 billion mark. This was a significant milestone for DAI and signaled the widespread adoption of a decentralized stablecoin. That same year, the MakerDAO community made significant strides toward fully decentralizing protocol governance. The Maker Foundation officially began transferring its authority to the DAO, effectively transferring control over DAI to a decentralized community rather than a single corporation.
- 2023–2024: The DAI ecosystem began supporting its collateral structure with Real World Assets (RWA) in addition to crypto assets. MakerDAO diversified some of its stablecoin reserves with traditional financial assets. For example, real-world assets such as certain bonds, commercial loans, or tokenized real estate began being accepted as collateral through smart contracts. This innovation further diversified DAI's collateral model and enabled it to leverage assets beyond the crypto market. MakerDAO, for example, aimed to increase protocol revenues by investing a portion of its DAI treasury in US Treasury bonds and collateralized loan agreements. This RWA initiative was considered a significant step toward bridging the gap between DeFi and traditional finance. As the RWA collateral model became more widespread in 2023-2024, confidence in DAI's stability and long-term sustainability also increased. Meanwhile, MakerDAO took significant steps within its Endgame plan that shaped the future evolution of DAI. In this context, NewStable (now the "Sky" protocol) was launched, and transitions from DAI to Sky began gradually. Alternatively, "PureDAI" was offered for those seeking an ideologically pure protocol.
- 2025: In the latest developments, on July 17–18, 2025, the US Congress passed the GENIUS Act, which addresses stablecoin regulation. This law introduces criteria for stablecoins, including high reserve transparency, 1:1 collateral, monthly reporting, independent auditing, and AML compliance. This suggests that global stablecoins like DAI will be more clearly framed under the US regulatory framework. However, due to DAI's inherent crypto-collateralization and decentralization, it may not be as directly affected as state-backed reserve stablecoins (like USDC and USDT). However, MakerDAO may need to increase its gloss to comply with the new process.
Why Is DAI Valuable?
In the cryptocurrency world, the concept of "value" isn't measured solely by price. Especially when it comes to stablecoins, factors such as the technology behind an asset, its security mechanisms, its use cases, and community support determine its true value. This is where DAI stands out among hundreds of stablecoins. Beyond simply being a coin pegged to $1, DAI represents a financial vision based on decentralization, transparency, and user control.
In today's rapidly changing economic environment, DAI offers a powerful alternative for individuals and institutions seeking an uncensored and accessible financial instrument. Whether it's protecting your savings, participating in DeFi protocols, or protecting against volatility, DAI is a valuable tool. While there are many stablecoins on the market, the key elements that make DAI so unique and valuable are:
Decentralized and censorship-resistant
DAI was designed as a completely decentralized stablecoin, meaning neither a bank nor a private company can control its transactions. Thanks to this structure, operated by smart contracts and a distributed network, no authority can seize or freeze the DAI in your account. This censorship resistance provides a significant advantage, especially for individuals living in authoritarian regimes or those with limited financial access. DAI is not just a cryptocurrency; it is also a powerful symbol of digital financial freedom.
Price Stability
Is DAI stable? Yes, DAI's primary goal is to always maintain its value at $1. Its value is protected by smart contracts and collateral structures that ensure the balance between supply and demand. This price stability makes it a reliable bridge, especially among DeFi coins. If you seek a stable value in volatile market conditions, DAI can be both a safe haven and a powerful tool for your financial transactions. DAI is particularly popular in DeFi protocols for transactions such as borrowing and lending, yield farming, or savings.
Transparent Collateral Structure
DAI has no hidden reserves or assets held behind closed doors. All collateral is clearly visible on the Ethereum blockchain. Each DAI is backed by overcollateralized assets on the blockchain, making it highly reliable within the collateralized stablecoin model. Anyone can examine the system's reserves and collateral ratios in real time. This transparency grounds DAI on a solid foundation not only from a technological perspective but also from a moral perspective.
Created by Users
There is no company or central institution that issues DAI; you generate it. When you deposit the appropriate collateral (e.g., ETH, USDC, RWA-backed tokens) into the MakerDAO system, the system returns DAI in return. This model transforms users from passive observers of the financial system into active producers. This feature is particularly revolutionary for individuals who lack access to traditional banking services. Creating your own stablecoin, locking collateral in a Maker vault, and receiving DAI in return provides liquidity and opens the door to participating in a decentralized economy.
Community-Based Governance
DAI's fate is not in the hands of a few individuals or companies. The MakerDAO community decides how the system operates. MKR token holders, through their voting rights, have a say in many matters, from collateral ratios and interest adjustments to the support of new assets and system updates. This allows the protocol to develop within a democratic framework called Maker governance. Everyone who uses DAI is also part of the ecosystem that governs it. This participatory model makes DAI more than just a digital asset; it also becomes a community initiative.
For the reasons mentioned above, DAI is valuable not only from a technical perspective but also from a philosophical perspective. As a living answer to the question "What is a decentralized stablecoin?", DAI has become an important tool for those seeking financial freedom and transparency. In the DeFi world, DAI has been integrated into many projects as a successful representative of the collateralized stablecoin model. For example, DAI has become one of the most borrowed/lent assets on many lending platforms (Aave, Compound, etc.). Furthermore, DAI liquidity pools are popular on decentralized exchanges, and DAI is frequently preferred in yield optimization protocols. All these integrations place DAI in a critical position among DeFi coins. In this way, DAI finds itself among the largest stablecoins in terms of market value as of today.
Who is the Founder of DAI?
The MakerDAO protocol, which gave rise to DAI, was initiated by Rune Christensen. Christensen is a Danish entrepreneur who conceptualized the Maker project in 2014. The idea of MakerDAO and DAI stemmed from Rune Christensen's vision of creating a decentralized stablecoin.
In the project's early years, the Maker Foundation, founded under Rune Christensen's leadership, served as the foundation supporting the protocol's development and adoption. The Foundation facilitated DAI's successful growth by laying the groundwork for software development, marketing, and legal matters. However, Christensen had planned from the outset that this foundation would be temporary. Indeed, in 2021, the Maker Foundation dissolved itself, transferring all authority and responsibilities to the MakerDAO community. This step symbolized the transition to fully decentralized governance of DAI and the Maker protocol.
Today, there is no single person or company that can be considered the "owner" of DAI. The MakerDAO community is the driving force behind the development and maintenance of DAI. Various working groups and volunteer contributors within MakerDAO ensure the protocol's continuity. Governance decisions are made by the votes of MKR token holders, and each participant, including Rune Christensen, influences the DAI coin solely based on their voting power. In short, when asked who owns the DAI coin, the most accurate answer is that DAI is a collective project, controlled by a distributed community. Rune Christensen is historically known as the founder of MakerDAO and the originator of DAI.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some short answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about DAI:
- How does DAI remain stable?: DAI is a stablecoin whose value is intended to remain at $1. To maintain this stability, DAI is backed by a collateral mechanism managed by smart contracts. Each DAI is backed by excess collateral, and the MakerDAO protocol keeps the price of DAI around $1 thanks to tools like interest rates and arbitrage opportunities.
- Who owns the DAI coin?: DAI has no specific company or individual owner. DAI is managed by the decentralized community called MakerDAO and generated by users. While Rune Christensen and the Maker Foundation pioneered its initial creation, today DAI remains entirely decentralized and controlled by the MakerDAO community.
- Is DAI centralized or decentralized?: DAI is a fully decentralized stablecoin. This means it is not governed by a bank, corporation, or central authority. Its rules and operations are fixed by code on the blockchain and overseen by the community, making DAI more resistant to external interference than centralized stablecoins.
- What is the difference between DAI and USDT or USDC?: Stablecoins like USDT and USDC are issued by centralized entities (companies like Tether and Circle) and are typically based on actual dollar reserves held in banks for each coin. DAI, on the other hand, is created in exchange for crypto collateral without a central issuer. Therefore, DAI's reserves are transparent and reside on Ethereum, while USDT/USDC reserves are based on company statements and audits. Furthermore, while USDT/USDC issuers can freeze specific addresses, DAI lacks such a central control mechanism.
- How much collateral is required to generate DAI?: To generate DAI, you always need to deposit collateral worth more than the amount of DAI you generate. The system typically requires a minimum collateral ratio of at least 150%. For example, if you want to generate 100 DAI, you must deposit at least $150 worth of collateral (e.g., Ether). The collateral ratio can vary depending on the type of asset you use and is determined by the MakerDAO administration.
- What happens if collateral falls in the DAI system?: If the value of the asset you deposit as collateral falls below the minimum collateral ratio, your position becomes risky. In this case, the system may initiate a process called liquidation. During liquidation, a portion of your collateral is automatically auctioned to pay off your debt (the DAI you've generated) and, if necessary, a penalty fee is charged. This ensures that DAI remains fully backed in the market. Users can prevent liquidation by adding additional collateral or partially repaying their DAI debt when the collateral value begins to decline.
Follow the JR Kripto Guide series for detailed information about DAI and other decentralized stablecoins.